Project Arduino – Boards
If you’re interested in electronics and programming, Arduino is a great platform to explore. I started my journey by getting an Arduino Uno board and some basic components, such as LEDs, resistors, and jumper wires. If you’re just starting out, I recommend getting an Arduino Uno as it is the most common board and has a lot of resources available online. During this course, I will be posting blog posts that can help me as a reminder and helps me to understand more about the platform.
So to start off, I will be using the Arduino Uno Rev3.
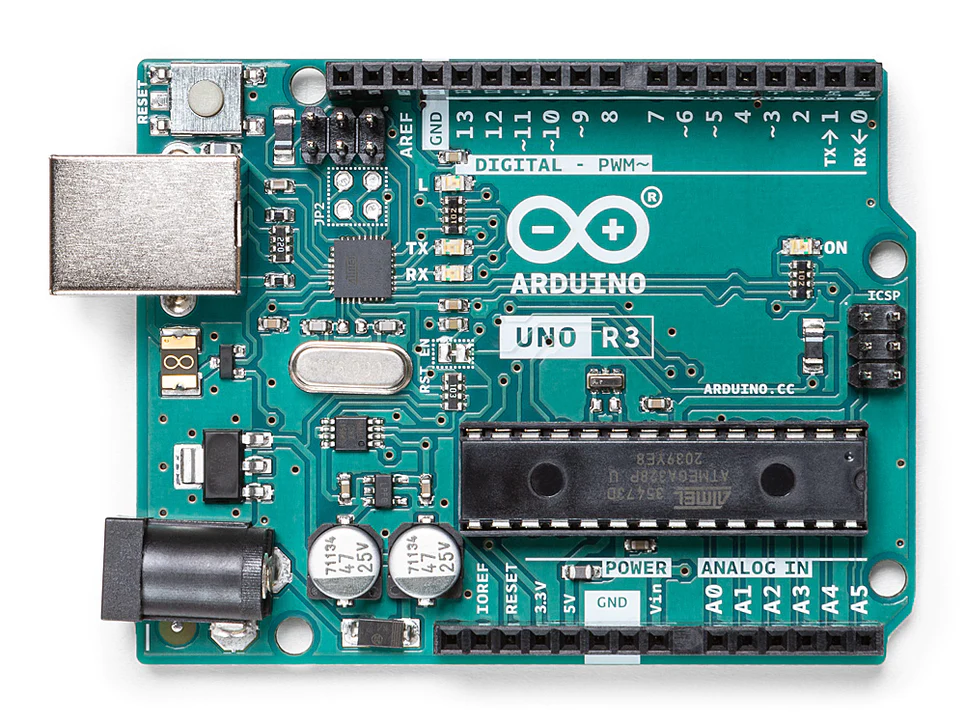
Ports
In the beginning, it’s good to know the difference between the ports that are available on a board. An Arduino microcontroller has both analog and digital ports, which are used for different types of input and output.
Analog ports are used to measure continuous electrical signals, such as those from a sensor that detects temperature or light. Analog inputs on an Arduino are labeled with an “A” followed by a number (e.g. A0, A1, A2), and can read values between 0 and 5 volts. The analog input pins convert the voltage values into digital values that the microcontroller can understand and process.
Digital ports, on the other hand, are used to send or receive binary signals, which are either on or off (1 or 0). Digital pins on an Arduino are labeled with a number (e.g. 0, 1, 2, 3) and can be used for both input and output. They are typically used for devices that need to be controlled digitally, such as LEDs, switches, and relays.
The main difference between analog and digital ports is the type of signal they can read or send. Analog ports read and convert continuous electrical signals, while digital ports read or send binary signals.
Some other examples of Arduino boards with the number of ports.
Arduino Leonardo
20 Digital ports & 12 Analog ports
Arduino Zero
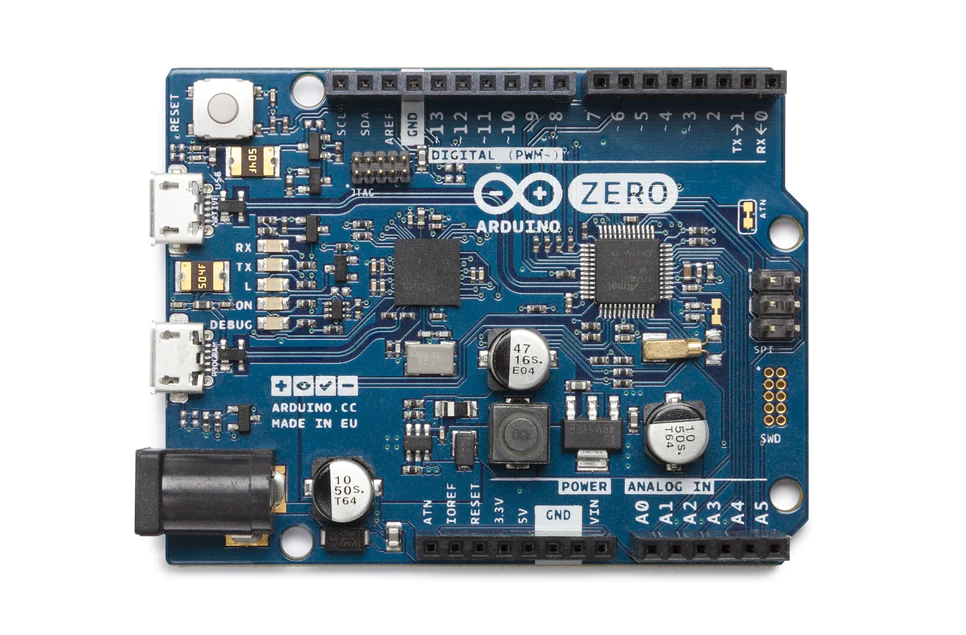
20 Digital ports & 1 Analog port
Arduino Micro
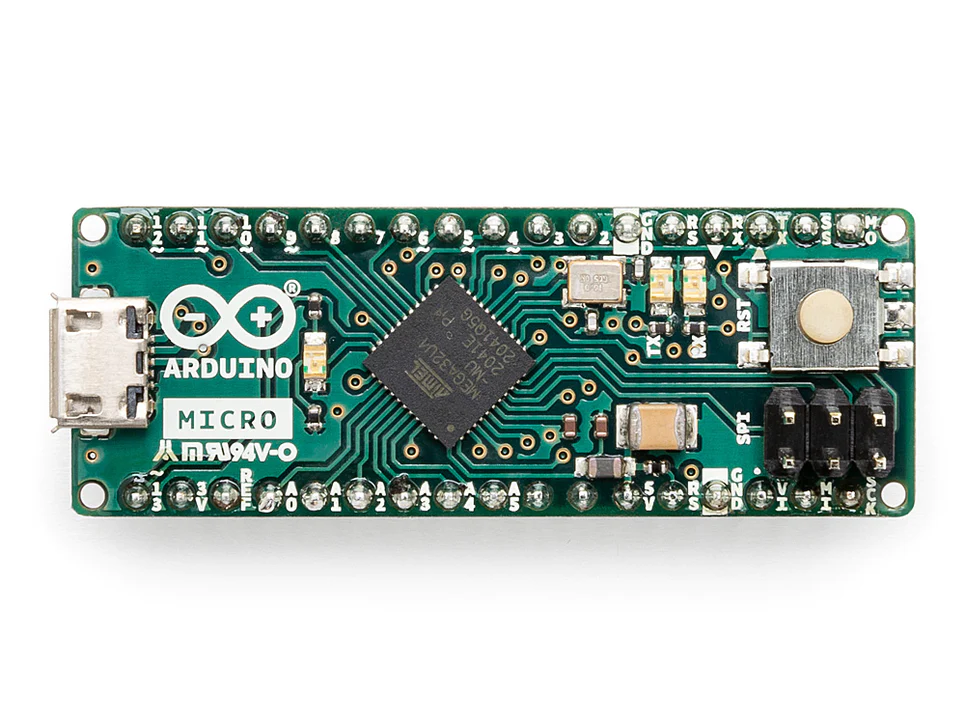
20 Digital ports & 12 Analog ports
